Health crazes and dieting encourage weight-loss at all costs. Some of the most common terms used in health and fitness terminology include fat loss or fat burn, etc. It is, therefore, common to be misinformed about fats. Fat is essential for our body. It is good to know the difference between ‘good’ fats and unhealthy fats. Fatty acids are an example of ‘good’ fats, which help maintain the suppleness of the skin, provide fat soluble vitamins and release energy to the body. In contrast, trans fats, which clog the arteries and harm the heart are an example of ‘bad’ fats. Omega-3 fatty acids are ;’good’ fats that do not lead to weight gain, rather they provide a myriad of health benefits. In some cases, the ‘good’ fats and the ‘bad’ fats may work synergistically to provide some health benefits to the body. This article focuses on the ‘good’ fats, especially Omega-3 fatty acids.
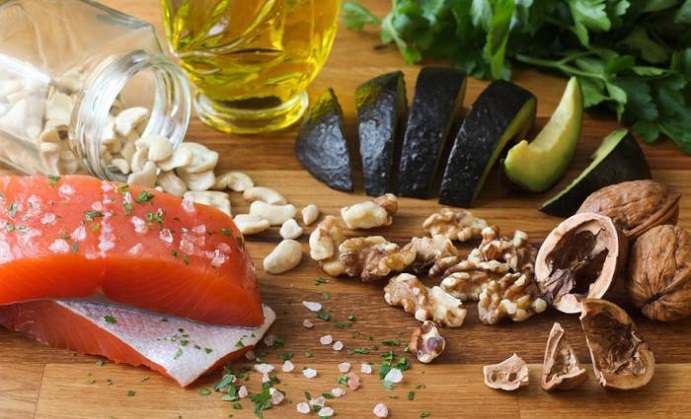
 Omega-3 is comprised of three distinct acids known as A-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Each one provides a range of health benefits. A-Linolenic acid known as AHA can be sourced from flaxseed oil, sacha-inchi oil, algal oil, clary sage seed oil, echium oil, hemp oil and soybeans, etc. Eicosapentaenoic acid abbreviated as EPA, is commonly found in fish oils, egg oil, squid oils, and krill oil. Docosahexaenoic acid referred to as DHA can be found in marine oils. Mothers who nurse their babies, enrich them with a rich source of DHA through breast-milk.
Omega-3 is comprised of three distinct acids known as A-linolenic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid. Each one provides a range of health benefits. A-Linolenic acid known as AHA can be sourced from flaxseed oil, sacha-inchi oil, algal oil, clary sage seed oil, echium oil, hemp oil and soybeans, etc. Eicosapentaenoic acid abbreviated as EPA, is commonly found in fish oils, egg oil, squid oils, and krill oil. Docosahexaenoic acid referred to as DHA can be found in marine oils. Mothers who nurse their babies, enrich them with a rich source of DHA through breast-milk.
A typical American diet has excessive Omega-6 fatty acids, which are available in vegetable oils such as corn oil, safflower oil, soybean oil, as well as poultry and eggs. One of the main acids of Omega-6 is Gamma Linolenic Acid (GLA) which has the properties to treat various medical conditions, including eczema, dermatitis, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, atherosclerosis, diabetes, obesity and chronic inflammation. However, Omega-6 must be taken only in moderation. Otherwise, it may affect the absorption of Omega-3 fatty acids in the body.
 Seafood especially certain kinds of fish may contain the high level of Omega-3 fatty acids. However, fish rich in Omega-3 but high in mercury may be harmful to health. So it is important to choose fish varieties with low levels of mercury and high levels of Omega-3. Seafood is not very common in the average diet. Hence, intake of fish and inclusion of Omega-3 in one’s diet is very low. Even if one takes fish, high mercury levels in the fish may cause adverse effects. Since the American diet contains high levels of Omega-6, it may nullify the effects of Omega-3 fatty acids. So it is important to take Omega-3 and Omega-6 in a three-to-one ratio for optimal benefit.
Seafood especially certain kinds of fish may contain the high level of Omega-3 fatty acids. However, fish rich in Omega-3 but high in mercury may be harmful to health. So it is important to choose fish varieties with low levels of mercury and high levels of Omega-3. Seafood is not very common in the average diet. Hence, intake of fish and inclusion of Omega-3 in one’s diet is very low. Even if one takes fish, high mercury levels in the fish may cause adverse effects. Since the American diet contains high levels of Omega-6, it may nullify the effects of Omega-3 fatty acids. So it is important to take Omega-3 and Omega-6 in a three-to-one ratio for optimal benefit.
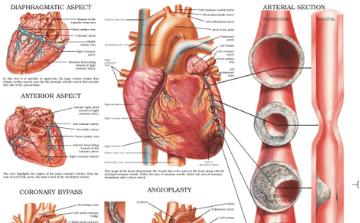
Including Omega-3 in one’s diet can also help treat medical conditions such as autoimmune disorders, heart diseases, brain diseases and anxiety related disorders. You can check with a physician and make sure to include the right amount of Omega-3 in your food, either as a supplement or through plant and animal sources to take full advantage of this nutrient.
Do you want to find an effective Omega-3 supplement? Check out our top rated Omega-3 products